The AbD Making Moves are a set of observable or actionable “moves” that learners and educators can use to help design maker-centered learning experiences, and to support, observe, document, and assess maker-centered learning.

The AbD Making Moves are a set of observable or actionable “moves” that learners and educators can use to help design maker-centered learning experiences, and to support, observe, document, and assess maker-centered learning.


Students from King Middle School in Portland, Maine, explain the importance of looking closely in a maker-centered classroom.
Video by Alex Coppola

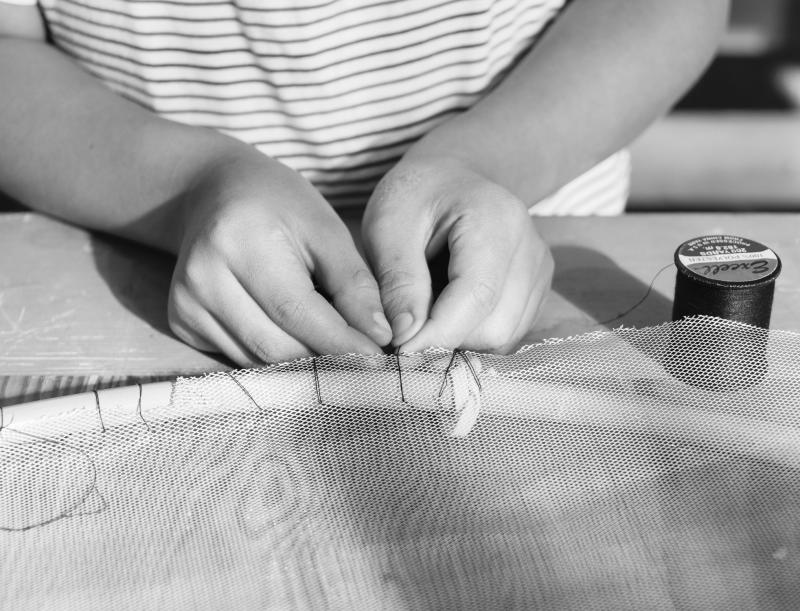
This thinking routine helps learners slow down and look closely at a system. In doing so, young people are able to situate objects within systems and recognize the various people who participate—directly or indirectly—within a particular system.

这个思考模式通过帮助学生近距离观察某个物品/系统的细节,考虑不同的使用者和利益相关者不同的观点角度,以反思自己和这个物品/系统的关系来探究其中的关联性。
This routine encourages learners to slow down and make careful, detailed observations as they look beyond the obvious features of an object or system and think about how it works. This thinking routine can help foster curiosity as children notice details, ask questions, make connections, and identify topics for future inquiry.

Jaime Chao Mignano is a Senior Practitioner Specialist on the JusticexDesign (JxD) project, and an ongoing leader in the project's conception and development, including developing tools and supporting educators to apply the emerging JxD framework in their contexts.
We find ourselves in a thorny historical moment, in the United States and around the world. Like my colleagues on the JusticexDesign project—and like many educators—I wonder: How will we support our students in deepening their understanding of the world around them and exploring the complex interplay of histories we are taking part in? In the US, we are debating the fate of American monuments, the legacy of American founders, and the impact of America’s own super story on the lived experiences of its people. How might we offer a path of agency to our students that champions historical honesty? And as we guide our students in considering colonial legacies, migration crises, and global economic injustice, what are some ways we might actively value the voices of communities adding their own truth to a contested history, even at terrible risk?
Artist Titus Kaphar’s work offers a rich model, pieces “that are honest, that wrestle with the struggles of our past but speak to the diversity and the advances of our present.” WIS History teacher Nora Brennan, a colleague in Agency by Design's Making Across the Curriculum project, and I had been struck by Kaphar’s 2017 TED Talk, “Can Art Amend History?” He asks, with his own children in mind, “What is the impact of these kinds of paintings on some of our most vulnerable in society, seeing these kinds of depictions of themselves all the time?” Kaphar concludes by urging us to “amend our public sculptures, our national monuments” in order to expand and deepen our historical narrative.
In the fall of 2018, Nora took her history class to visit the Titus Kaphar collection in the “UnSeen: Our Past in a New Light” exhibit in the National Portrait Gallery. This experience was clearly powerful for students—we could sense that Kaphar’s artworks were shifting their gazes, pointing them to an actively unfolding dialogue on American history. Nora knew she wanted her students to connect more deeply to Kaphar’s philosophy of historical amendment. She combined this art exhibit and the history lessons she was teaching on the Civil War and Reconstruction as the foundation to challenge students to research a Civil War monument and reimagine it.
At the same time, Nora knew it was important to contextualize this project in the very active conversation in the U.S.—and around the world--about monuments and public memory. The controversy around Civil War monuments was and is a real current event—many city and state governments have been taking steps to address the symbolic presence of historical racial terror embedded in public spaces by tearing down monuments, renaming streets and buildings, etc. We wanted students to situate their thinking within these substantive critiques - not to attempt reconciliation but to explore their own perspective.
Nora drew on the Agency by Design framework to build her students’ sensitivity to the design of monuments and portraits. She knew that historical artworks can both express and obscure, offering us complex legacies that we can guide students in unpacking and probing. We wondered what maker empowerment might look like as students approach a portrait of Robert E. Lee or a statue of John. C. Calhoun.
Participants at the Arts Education Partnership National Forum consider the role of the arts in maker-centered learning experiences.

The Agency by Design guide to implementing maker-centered teaching and learning
Maker-Centered Learning provides both a theoretical framework and practical resources for the educators, curriculum developers, librarians, administrators, and parents navigating this burgeoning field. Written by the expert team from the Agency by Design initiative at Harvard's Project Zero, this book
A surge of voices from government, industry, and education have argued that, in order to equip the next generation for life and work in the decades ahead, it is vital to support maker-centered learning in various educational environments. Maker-Centered Learning provides insight into what that means, and offers tools and knowledge that can be applied anywhere that learning takes place.

Esta rutina de pensamiento ayuda a los estudiantes a ir lentamente y observar detallada y cuidadosamente, al animarlos a mirar más allá de las características obvias de un objeto o sistema. Esta rutina de pensamiento estimula la curiosidad, plantea preguntas y hace evidente otras áreas para continuar la investigación.